When you need to automatically notify objects about change of one object, observer pattern comes to help you. As additional benefit, we will get loosely coupled code and also we can dynamically add or remove observer objects.
Description
Observer design pattern defines one-to-many relation. That relation has the property, that when state changes on “one” object, it will notify “many” objects. To listen to this changes, object must subscribe to object (also they can unsubscribe from the object). Implementation of observer pattern is illustrated in the image below:
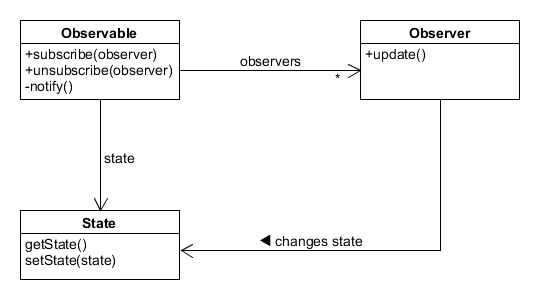
- Observable - Its state is observed and notifies observers about a change of state.
- Observer - Attaching to observable by method subscribe and is notified over method update, when a change of state of observable occurs.
- Update - This method is called when observable changes state.
- Notify - This method is called when state in observable is changed. In implementation, this method will iterate through all observers and call their method update.
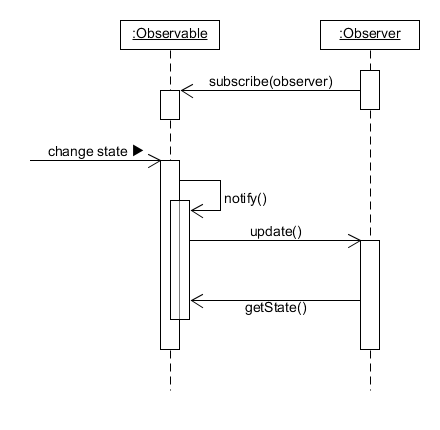
Responsibilities
- Responsibility of observable is maintaining list of observers and notify them about change of state.
- Responsibility of observer is to register (and unregister) themselves on observable and update their state when they are notified.
Push or pull type?
There can be two types of implementation style for distributions of changes. The only difference between them is in the transmission of information.
- Pull - In pull type, observers will ask observable for information in update method. So, received information is the responsibility of the observable.
- Push - Push type has given information as an argument in update method.
Which implement?
In case when the observable needs to send large amount of data to observer, push style might be inefficient. To mitigate this, we can send only required information by the type of observer, but in this case, observable would must know the differences between observers. This can lead to more coupled code, then loosely coupled. But on the other hand pull model is more usable for reuse, then push model, which is less efficient.
Who calls notify method?
The communication between observer and observable is done by notifying method. But who calls it? It can be called by the observer and also by observable self. Usually is called by observable, when change occurs. But this can lead to the very frequent calling of notify method. So, calling it in observer will be more efficient, than by observable self, because it can be called when it is necessary.
Usage
Observer pattern is implemented and used a lot in Event Driven Programming and also has an important part in MVC pattern. So, it is implemented in almost all GUI frameworks and libraries. Also, it is enhanced and implemented in Reactive Programming.
Reactive programming relation
Reactive programming use observer design pattern extended with Dispose design pattern and Iterator design pattern. And is principally implemented everywhere in Reactive programming.
Conclusion
The observer design pattern is here to solve problems when we need to notify numerous objects when the state of observable change, and that nedd to be done automatically. Observer creates loosely coupled relation, because observable and the observer does know nothing about each other. And also Observer pattern is the base of Reactive Programming.